Car-title lending — making expensive loans secured by the title of a vehicle a borrower owns out-right — has become a multi-billion dollar industry in the U.S. over the last decade. CRL estimates that car-title lenders generate nearly $2 billion in loans annually, with borrowers paying more than $4 billion in fees — twice the amount loaned — in the process. While borrowers in most states are protected from these high-cost loans, 21 states permit these products that trap borrowers in debt and put one of their most significant assets on the line.
This chapter discusses key abuses in car-title lending, including a lack of underwriting, balloon payments, high APRs, loan churning and the threat of repossession. This chapter also updates recent estimates on the size of the car-title lending market and policy recommendations for state legislatures and federal regulators.
Car-Title Loans: A Road to Nowhere [Infographic]
By the numbers: this graphic shows the figures behind the debt-trap nature of car-title loans, the consequences for borrowers who don't make their balloon payments on time, and the multi-billion dollar industry that benefits from this predatory practice.
Car-Title Borrowers' Two Bad Choices [Infographic]
When a Car-Title Loan payment is due - typically in full, after 30 days - a borrower who can't make the balloon payment is faced with two choices. Both can send the borrower deeper into a cycle of debt.
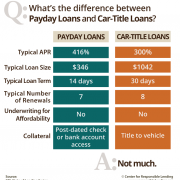
Car-Title Loan or Payday Loan? [Infographic]
What's the difference between car-title loans and payday loans? Not much, as this graphic shows...